
Java 14: New Features
Introduction.
The latest release of the Java SE platform - JDK 14 , was made generally available on the 17th of March 2020. This release has been in the planning stage since June 2019 when the Expert Group was formed.
Just like in Java 12 and 13, new manageable features are present in version 14 also. Oracle Engineers and the OpenJDK Community’s collaboration, development, and reviews take credit for the best features of version 14.
Every six months, Oracle releases a new version of Java to increase innovation among the developer community. It brings exciting new features to enterprise applications.
Java 14 has introduced 16 enhancements and 69 API elements. These new features will help to improve the efficiency of Java applications significantly.
In this article, we will discuss some of the most important features of the latest release of Java.

305 - Pattern Matching for instanceof(Preview)
This is a preview feature, which means that developers can try out this feature without having it as a part of the JAVA SE standard. Preview features allow developers to find and report errors in new features and to allow suggestions.
JEP 305 adds pattern matching to the instanceof operator. This will help developers to improve their productivity as this ensures concise code rather than boilerplate code, which is inserted in many places with minimal alteration.
So what’s new in this feature? The ‘instanceof’ operator tests the type of a given object against different types. This method is useful when you are not sure of the type of an object. However, the main drawback of this feature is that we need to explicitly cast to each type in order to compare against it.
This drawback is eliminated in the new release by introducing a variable instead of having to cast explicitly.
343 - Packaging Tool
Java applications can be packaged and installed just like other programs, with the use of the packaging tool. The jpackage tool introduces this feature and packages all the dependencies required to run the application. Given below are the package types supported for each platform:
- Linux - deb, rpm
- Windows - msi, exe
- macOS - pkg, dmg
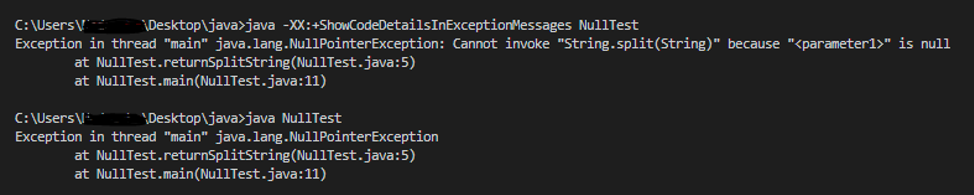
358 - Helpful NullPointerExceptions
NullPointer exceptions are thrown when you try to access an Object reference that is not initialized. Up to now, Java used to send a detailed message of this exception that sometimes confused developers as they were unable to find where exactly the error occurred.
In the latest release, the JVM specifies precisely which object is null. This helps to troubleshoot the program better and reduces confusion.
To test this feature, try, java -XX:+ShowCodeDetailsExceptionMessages
359 - Records
Records are new data classes or type declarations introduced with the freshly released version of Java. This feature answers some of the complaints made about Java saying that it is too wordy to verbose. Consider the example below, for instance. It has too many lines to accomplish a simple task.
A particular record consists of a name and state description.
record Point(int x, int y) { }
Output:
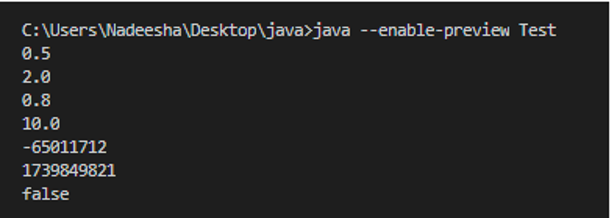
The record class is final (immutable) with all of its fields, and it automatically picks up a public constructor, read accessor methods, toString() implementation, equals(), and hashCode(). As this is a preview feature, you will have to use –enable preview when running the program.
361 - Switch Expressions
In the earlier versions of Java, switch statements without the “break” keyword would result in a situation called “fall through”. In a fall through, all the case statements will execute even after the relevant case statement is executed. It was essential to include a break keyword in each case to avoid this situation as shown in the code below:
Also, in instances where multiple cases would give the same output, cases had to be added individually as given above.
In Java 14, you can execute case statements with no fall through using arrows. When you declare a case label with an arrow (such as “case x - > “), only the code placed adjacent to it will be executed, which means that there will be no fall-through. All unnecessary executions can be eliminated while reducing the number of lines of code required through the use of commas.
364 - ZGC on macOS and 365 - ZGC on Windows
JEPS link for macOS & JEPS link for Windows
ZGC is the Z Garbage Collector, which is scalable and has low latency. It makes sure that pause times do not exceed 10ms and that they do not increase with the heap of live-set size. Also, it deals with heaps of 8MB to 16TB. As this ensures concurrent operations and uses load barriers, it enables Java threads to execute without delay while it does the heavy work.
This feature was only available on Linux up to now. But with this new release, even Windows and macOS platforms can make use of the ZGC.
JEP 368 - Text Blocks (Second Preview)
The Text Blocks feature is being previewed for the second time subsequent to its introduction in JDK 13. It offers the benefit of allowing strings that span multiple lines of source code without the need for escape characters.
In JDK 14, two new escape sequences have been introduced based on feedback received for the feature in its predecessor. These are for <end-of-line> suppressing line terminations and \s single spaces. Let’s look at an example:
Text Blocks improve the readability of strings that denote code from non-Java languages. Support is provided for migration from string literals by ensuring that new constructs can express strings as string literals, interpret the same escape sequences, and allow for manipulation similarly to a string literal.
370 - Foreign Memory Access API
Developers face a conundrum when they have to access foreign memory as they have to choose between a safe but limited and less efficient path such as ByteBuffer and an unsupported and dangerous API such as “Unsafe” which is efficient. In the latest version, JEP introduces a safe and methodical API to access foreign memory, and it has three major abstractions.
- Memory Segment - This models a contiguous (adjacent) memory region with bounds.
- Memory Address - This is an offset in a segment.
- Memory Layout - This describes the contents in a memory segment programmatically.
Developers can now make a better choice without needing to be concerned about the limitations and dangers of accessing foreign memory.
Conclusion
Java 14 consists of exciting new features such as changes to language syntax, new APIs, and changes to the JVM and Java libraries that make our coding journey easier and reduces verbose coding. You can find more details about this release and the full list of new features on the official Oracle blog.
Preview features are an important and useful way to obtain developer consensus regarding new features and deprecations. For example, the enhanced Switch statement was previewed in JDK 12 and 13 and then introduced as a permanent feature in JDK 14 as it was well accepted by developers. The Java team requests developers to report issues and suggestions via the Oracle Java Bug Database.
Be free to ask us any questions.
Stay updated. Stay Shardik. Try new.
